As we approach retirement age, we have a slew of options available to us; we can start withdrawing from our nest egg, claim Social Security benefits, or a combination of both. We also have the opportunity to continue working or not while claiming Social Security benefits. The decision as to when to claim Social Security can be complex, with numerous factors to consider. While there may be compelling reasons to take benefits as soon as possible, there are also strong arguments for delaying until the age of 70. This delicate balance of considerations presents a challenging yet vital aspect of retirement planning.
When does it make sense to take benefits early, and when does it make sense to delay? Naturally, it all depends on your individual circumstances and goals. This article delves into the intricacies of each possible decision and highlights the differences with a technical case study to help us make the case for each.
Social Security Benefits
To fully understand our options, it is critical we understand exactly how Social Security works. Social Security benefits are based on an individual’s lifetime earnings, and the amount received depends on the age at which you claim benefits.
Up to 35 years of your earnings are adjusted to account for changes in the standard of living during your working life. These indexed earnings are used to find the average indexed monthly earnings (AIME). To compute the AIME, the years with the highest indexed earnings are selected, added up, and divided by the total number of months in those years, then rounded down to the next dollar. This AIME forms the basis for determining your primary insurance amount (PIA), which becomes the figure for your benefits.
In 2023, you can claim benefits as early as 62 years old, though you are facing a 30% reduction in benefits – for life. The current full retirement age is 67, at which point you get 100% of your benefits, ostensibly for a more extended period. If you can manage to delay benefits beyond that, you’ll see an 8% yearly increase up to the age of 70, where you can maximize your benefits to 124% – again, for life, albeit with a shorter overall duration.
Social Security Taxation
However, if you continue working while receiving Social Security benefits, your benefits may get taxed at a higher rate compared to if you are simply withdrawing from your various retirement accounts. How they will be taxed depends on the tax status of your retirement accounts. Roth withdrawals, for example, likely won’t affect the taxation of your Social Security benefits as much as Traditional account withdrawals.
If your income is high enough, either from working or retirement withdrawals or other income sources, you may have to pay federal income taxes on your Social Security benefits. The amount taxed is up to 85% of your benefits as follows:
Individual Filers:
Income between $25,000 and $34,000: up to 50% of benefits may be taxable.
Income over $34,000: up to 85% of benefits may be taxable.
Joint Filers:
Combined income between $32,000 and $44,000: up to 50% of benefits may be taxable.
Combined income over $44,000: up to 85% of benefits may be taxable.
The Case for Claiming Social Security Early
So when may you want to start taking benefits early? Perhaps you have urgent financial requirements, such as medical bills, debts with high-interest rates, or to support dependents. You may also be concerned that future legislation will reduce or eliminate Social Security altogether, so you want to receive those benefits while you still can, as unlikely as this scenario is. Health considerations may also play a significant role. If you are facing a shortened life span, taking those funds while you can may make sense.
The Case for Delaying Social Security
However, as mentioned above, delaying benefits may be advantageous for various reasons, particularly if you predict a long life span. If you live well into your 90s, it may be difficult to stretch out your savings that long, at which point the extra funds made available to you by increasing your benefits can ultimately pay off, providing you with a much-needed cushion in your later days.
Delaying benefits may ease your tax burden as well if you stop working and your only taxable income is from your retirement account withdrawals.
Spousal Considerations
Depending on both spouses’ earning records, age, and health considerations, it might be optimal for one to claim benefits early while the other delays. This could enhance the overall benefits received, especially if immediate financial needs exist or there are concerns about life expectancy.
Furthermore, if there’s a substantial disparity in earning history between the spouses, delaying benefits for the higher-earning partner may increase the survivor benefits that would be payable to the other spouse in the event of their death.
The Break Even Point
By putting all these points together, we can create a break-even point to help you determine the best course of action.
In an early claiming scenario for the year 2023, let’s consider an individual who chooses to begin taking Social Security benefits at the age of 64 and 2 months. The monthly benefit amount in this instance is $2,113.00, leading to an annual benefit of $25,356. This amount is not static; we will assume an additional 3% each year to adjust for cost of living increases.
In a scenario where an individual opts to delay claiming Social Security benefits until age 70 in the year 2029, the monthly benefit amount grows to $3,610.00, resulting in an annual benefit of $43,320. Like the early claiming scenario, there is a cost-of-living adjustment (COLA) increase of 3% each year.
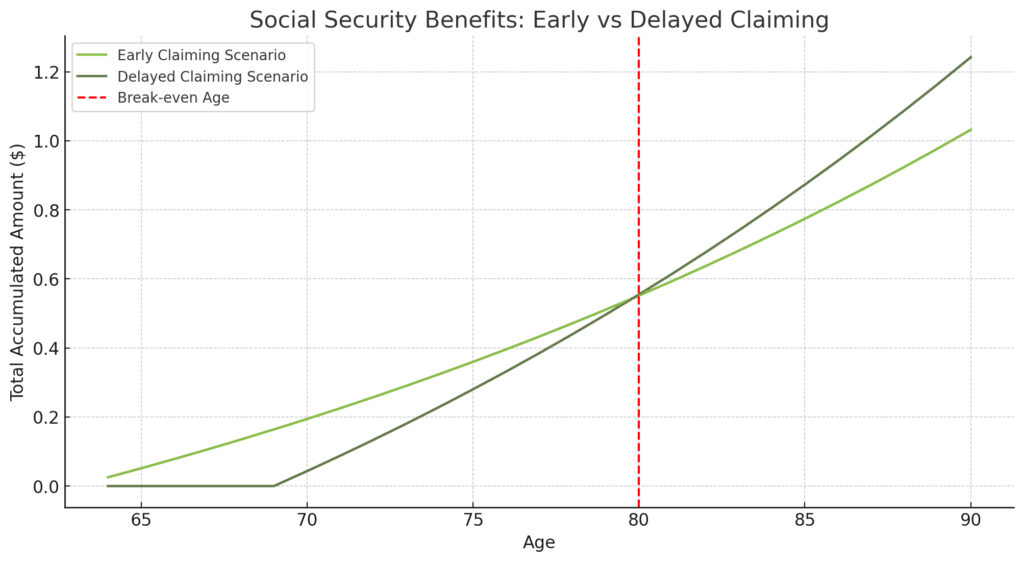
The break-even analysis depicted in the line graph above clearly compares the early and delayed claiming scenarios for Social Security benefits, taking into account a 3% annual cost-of-living adjustment until the age of 90.
At the break-even age of 80, the early claiming scenario yields a total of $551,786.82, while the delayed scenario slightly surpasses it at $554,833.71. Beyond this age, the delayed claiming scenario proves more lucrative, accumulating more total benefits as you age.
If you feel that you will have a long life span and experience difficulties living off of your retirement savings at an advanced age, delaying benefits may be the most beneficial path for you.
Alternatively, if you feel that you won’t survive past 80 or you will have sufficient retirement savings and could make better use of your benefits at an early age, claiming benefits may be better for you.
Of course, these two scenarios are greatly simplified – factors like inflation, taxes, estate plans, and changing legislation can also significantly affect your decision on accepting benefits early or not. That’s why it’s vital to sit down with a financial advisor to hammer out every possible detail to help you reach the proper conclusion.
In Conclusion
As we’ve illustrated, the choice between choosing Social Security benefits early, at full retirement age, or delaying is an exceedingly difficult one, with numerous factors affecting it. Taxes, inflation, laws, health considerations, the size of your savings, and your marriage status all come together to form a dizzying web of possibilities and potential outcomes. It’s not a decision to be taken lightly, and the slightest nuances can significantly impact your financial stability and comfort in retirement.
Feeling overwhelmed by Social Security’s intricate web? You’re not alone. Navigating the complex waters of Social Security benefits requires a thorough understanding of various factors, and crunching the numbers and considering all the possible scenarios yourself may feel overwhelming and confusing.
The decisions awaiting you can be daunting, but that’s why we’re here. We can craft a strategy tailored to your unique needs, optimizing your retirement benefits at every life stage. Don’t delay – click the button below to begin your journey with us.













